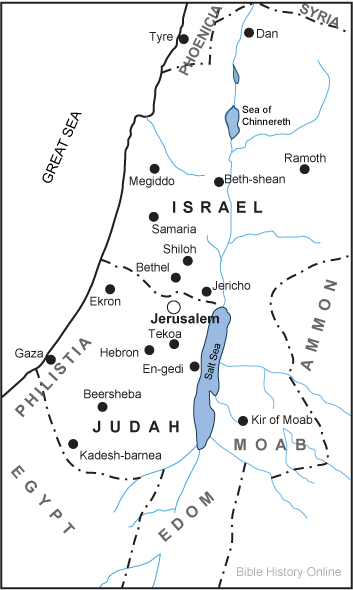
Israel and Judah
(Enlarge)
(PDF
for Print) (Freely Distributed)
Map of the Kingdoms of
Israel and Judah
After David and Solomon, the fame
and fortunes of Israel went downhill. The nation rebelled against
God and his laws. God might have destroyed Israel had He not
promised to Abraham a redeemer and He still planned to use the house
of David for this.
When Solomon died a civil war broke out as Solomon's sons and
generals fought for the throne. Rehoboam had his fathers blessing to
be the new king, but Jeroboam had more military influence. In the
end, Rehoboam took the southern half of the country and called it
"Judah". Jeroboam took the northern half and kept the name Israel.
Each claimed to be God's chosen king.
The Northern Kingdom of Israel
The Northern Kingdom consisted of
10 of the tribes (excluding Judah and Benjamin). It lasted for about
210 years until it was destroyed by Assyria in 722 BC. Its capital
was Samaria. Every king of Israel was evil. In the northern kingdom
there were 9 dynasties (family lines of kings) and 19 kings in all.
An average of 11 years to a reign. 8 of these kings met death by
violence.
The epitaph written over every one of its kings was:
I King 15:34
"and he did evil in the sight of the LORD, and walked in the way of
Jeroboam, and in his sin by which he had made Israel to sin."
It was king Ahab who introduced Baal worship to them.
I King
16:30-33 "Now Ahab the son of Omri did evil in the sight of the
LORD, more than all who were before him. And it came to pass, as
though it had been a trivial thing for him to walk in the sins of
Jeroboam the son of Nebat, that he took as wife Jezebel the daughter
of Ethbaal, king of the Sidonians; and he went and served Baal and
worshiped him. Then he set up an altar for Baal in the temple of
Baal, which he had built in Samaria. And Ahab made a wooden image.
Ahab did more to provoke the LORD God of Israel to anger than all
the kings of Israel who were before him."
Israel was carried away captive to Assyria in 722 BC and disappeared from history.
The Southern Kingdom of Judah
The Southern Kingdom consisted of 2 tribes (Judah and Benjamin). The kingdom extended in the north as far as Bethel, while in the south it ended in the dry area known as the Negev. Its eastern and western boundaries were the Jordan River and the Mediterranean Sea. Jerusalem was its capital and it lasted from about 922-586 B.C., Judah had somewhat of a better record. Only 8 of Judah's kings served God. These were: Asa, Jehoshaphat, Joash, Amaziah, Uzziah, Jotham, Hezekiah, and Josiah. The rest of the 20 kings were wicked. In the southern kingdom there was only one dynasty, that of king David, except usurper Athaliah from the northern kingdom, who by marriage, broke into David's line, and interrupted the succession for 6 years, 20 kings in all. An average of about 16 years to a reign.
After Josiah there was no hope for Judah, the last 3 kings were all evil. The Babylonians swept down upon Jerusalem in 597 BC and captured it. A second attack led to Jerusalem's second defeat in 586 BC. Captives from both campaigns were taken to Babylonia to mark the captivity of the Southern Kingdom.
The Kingdom of Israel
in Smith's Bible
Dictionary
III. History. --The kingdom of
Israel lasted 254 years, from B.C. 975 to B.C. 721. The detailed
history of the kingdom will be found under the names of its nineteen
kings. See chart of the kings of Judah and Israel, at the end of the
work. A summary view may be taken in four periods: (a) B.C. 975-929.
Jeroboam had not sufficient force of character in himself to make a
lasting impression on his people. A king, but not a founder of a
dynasty, he aimed at nothing beyond securing his present elevation.
Baasha, in the midst of the army at Gibbethon, slew the son and
successor of Jeroboam; Zimri, a captain of chariots, slew the son
and successor of Baasha; Omri, the captain of the host, was chosen
to punish Zimri; and after a civil war of four years he prevailed
over Tibni, the choice of half the people. (b) B.C. 929-884. For
forty-five years Israel wag governed by the house of Omri. The
princes of his house cultivated an alliance with the king of Judah
which was cemented by the marriage of Jehoram and Athaliah. The
adoption of Baal-worship led to a reaction in the nation, to the
moral triumph of the prophets in the person of Elijah, and to
extinction of the house of Ahab in obedience to the bidding of
Elisha. (c) B.C. 884-772. Unparalleled triumphs, but deeper
humiliation, awaited the kingdom of Israel under the dynasty of
Jehu. Hazael, the ablest king of Damascus, reduced Jehoahaz to the
condition of a vassal, and triumphed for a time over both the
disunited Hebrew kingdoms. Almost the first sign of the restoration
of their strength was a war between them; and Jehoash, the grandson
of Jehu, entered Jerusalem as the conqueror of Amaziah. Jehoash also
turned the tide of war against the Syrians; and Jeroboam II., the
most powerful of all the kings of of Israel, captured Damascus, and
recovered the whole ancient frontier from Hamath to the Dead Sea.
This short-lived greatness expired with the last king of Jehu's
line. (d) B.C. 772-721. Military violence, it would seem, broke off
the hereditary succession after the obscure and probably convulsed
reign of Zachariah. An unsuccessful usurper, Shallum, is followed by
the cruel Menahem, who, being unable to make head against the first
attack of Assyria under Pul, became the agent of that monarch for
the oppressive taxation of his subjects. Yet his power at home was
sufficient to insure for his son and successor Pekahiah a ten-years
reign, cut short by a bold usurper, Pekah. Abandoning the northern
and transjordanic regions to the encroaching power of Assyria under
Tiglath-pileser, he was very near subjugating Judah, with the help
of Damascus, now the coequal ally of Israel. But Assyria interposing
summarily put an end to the independence of Damascus, and perhaps
was the indirect cause of the assassination of the baffled Pekah.
The irresolute Hoshea, the next and last usurper, became tributary
to his invaders Shalmaneser, betrayed the Assyrian to the rival
monarchy of Egypt, and was punished by the loss of his liberty, and
by the capture, after a three-years siege, of his strong capital,
Samaria. Some gleanings of the ten tribes yet remained in the land
after so many years of religious decline, moral debasement, national
degradation, anarchy, bloodshed and deportation. Even these were
gathered up by the conqueror and carried to Assyria, never again, as
a distinct people, to occupy their portion of that goodly and
pleasant land which their forefathers won under Joshua from the
heathen. (Schaff Bib. Dic.) adds to this summary that "after the
destruction of the kingdom of Israel, B.C. 721, the name 'Israel'
began to be applied to the whole surviving people. No doubt many of
the kingdom of Israel joined the later kingdom of the Jews after the
captivity, and became part of that kingdom.--ED.)
Full Article
The Kingdom of Judah in Smith's Bible Dictionary
Judah, Kingdom of
Extent. --When the disruption of Solomon's kingdom took place
at Shechem, B.C. 975, only the tribe of Judah followed David, but
almost immediately afterward the larger part of Benjamin joined
Judah. A part, if no all, of the territory of Simeon, 1Sa 27:6; 1Ki
19:3 comp. Josh 19:1
and of Dan, 2Ch 11:10 comp. Josh 19:41,42
was recognized as belonging to Judah; and in the reigns of Abijah
and Asa the southern kingdom was enlarged by some additions taken
out of the territory of Ephraim. 2Ch 13:19; 15:8; 17:2 It is
estimated that the territory of Judah contained about 3450 square
miles.
Advantages. --The kingdom of Judah possessed many advantages
which secured for it a longer continuance than that of Israel. A
frontier less exposed to powerful enemies, a soil less fertile, a
population hardier and more united, a fixed and venerated centre of
administration and religion, a hereditary aristocracy in the
sacerdotal caste, an army always subordinate, a succession of kings
which no revolution interrupted; so that Judah survived her more
populous and more powerful sister kingdom by 135 years, and lasted
from B.C. 975 to B.C. 536.
History --The first three kings of Judah seem to have
cherished the hope of re-establishing their authority over the ten
tribes; for sixty years there was war between them and the kings of
Israel. The victory achieved by the daring Abijah brought to Judah a
temporary accession of territory. Asa appears to have enlarged it
still further. Hanani's remonstrance, 2Ch 16:7 prepares us for the
reversal by Jehoshaphat of the policy which Asa pursued toward
Israel and Damascus. A close alliance sprang up with strange
rapidity between Judah and Israel. Jehoshaphat, active and
prosperous, commanded the respect of his neighbors; but under
Amaziah Jerusalem was entered and plundered by the Israelites. Under
Uzziah and Jotham, Judah long enjoyed prosperity, till Ahaz became
the tributary and vassal of Tiglath-pileser. Already in the fatal
grasp of Assyria, Judah was yet spared for a checkered existence of
almost another century and a half after the termination of the
kingdom of Israel. The consummation of the ruin came upon its people
in the destruction of the temple by the hand of Nebuzaradan, B.C.
536. There were 19 kings, all from the family of David. (Population.
--We have a gage as to the number of the people at different periods
in the number of soldiers. If we estimate the population at four
times the fighting men, we will have the following table:
King ... Date ... Soldiers ... Population
David ...B.C. 1056-1015 ...
500,000 ... 2,000,000
Rehoboam ...975-957 ... 180,000 ... 720,000
Abijah ...957-955 ... 400,000 ... 1,600,000
Asa ...955-914 ... 500,000 ... 2,000,000
Jehoshaphat ...914-889 ... 1,160,000 ... 4,640,000
Amaziah ...839-810 ... 300,000 ... 1,200,000
Full Article
The Bible Mentions why God punished Israel:
II Kings
17:7-23 "For so it was that the children of Israel had sinned
against the LORD their God, who had brought them up out of the land
of Egypt, from under the hand of Pharaoh king of Egypt; and they had
feared other gods, and had walked in the statutes of the nations
whom the LORD had cast out from before the children of Israel, and
of the kings of Israel, which they had made.
Also the children of Israel secretly did against the LORD their God
things that were not right, and they built for themselves high
places in all their cities, from watchtower to fortified city. They
set up for themselves sacred pillars and wooden images on every high
hill and under every green tree. There they burned incense on all
the high places, like the nations whom the LORD had carried away
before them; and they did wicked things to provoke the LORD to
anger, for they served idols, of which the LORD had said to them,
"You shall not do this thing."
Yet the LORD testified against Israel and against Judah, by all of
His prophets, every seer, saying, "Turn from your evil ways, and
keep My commandments and My statutes, according to all the law which
I commanded your fathers, and which I sent to you by My servants the
prophets." Nevertheless they would not hear, but stiffened their
necks, like the necks of their fathers, who did not believe in the
LORD their God. And they rejected His statutes and His covenant that
He had made with their fathers, and His testimonies which He had
testified against them; they followed idols, became idolaters, and
went after the nations who were all around them, concerning whom the
LORD had charged them that they should not do like them.
So they left all the commandments of the LORD their God, made for
themselves a molded image and two calves, made a wooden image and
worshiped all the host of heaven, and served Baal. And they caused
their sons and daughters to pass through the fire, practiced
witchcraft and soothsaying, and sold themselves to do evil in the
sight of the LORD, to provoke Him to anger.
Therefore the LORD was very angry with Israel, and removed them from
His sight; there was none left but the tribe of Judah alone. . And
the LORD rejected all the descendants of Israel, afflicted them, and
delivered them into the hand of plunderers, until He had cast them
from His sight. For He tore Israel from the house of David, and they
made Jeroboam the son of Nebat king. Then Jeroboam drove Israel from
following the LORD, and made them commit a great sin. For the
children of Israel walked in all the sins of Jeroboam which he did;
they did not depart from them, until the LORD removed Israel out of
His sight, as He had said by all His servants the prophets. So
Israel was carried away from their own land to Assyria, as it is to
this day."
Read The Bible
- 1599 Geneva Bible (GNV)
- 21st Century King James Version (KJ21)
- American Standard Version (ASV)
- Amplified Bible (AMP)
- Amplified Bible, Classic Edition (AMPC)
- Authorized (King James) Version (AKJV)
- BRG Bible (BRG)
- Christian Standard Bible (CSB)
- Common English Bible (CEB)
- Complete Jewish Bible (CJB)
- Contemporary English Version (CEV)
- Darby Translation (DARBY)
- Disciples’ Literal New Testament (DLNT)
- Douay-Rheims 1899 American Edition (DRA)
- Easy-to-Read Version (ERV)
- English Standard Version (ESV)
- English Standard Version Anglicised (ESVUK)
- Evangelical Heritage Version (EHV)
- Expanded Bible (EXB)
- GOD’S WORD Translation (GW)
- Good News Translation (GNT)
- Holman Christian Standard Bible (HCSB)
- International Children’s Bible (ICB)
- International Standard Version (ISV)
- J.B. Phillips New Testament (PHILLIPS)
- Jubilee Bible 2000 (JUB)
- King James Version (KJV)
- Lexham English Bible (LEB)
- Living Bible (TLB)
- Modern English Version (MEV)
- Mounce Reverse Interlinear New Testament (MOUNCE)
- Names of God Bible (NOG)
- New American Bible (Revised Edition) (NABRE)
- New American Standard Bible (NASB)
- New American Standard Bible 1995 (NASB1995)
- New Catholic Bible (NCB)
- New Century Version (NCV)
- New English Translation (NET)
- New International Reader's Version (NIRV)
- New International Version - UK (NIVUK)
- New International Version (NIV)
- New King James Version (NKJV)
- New Life Version (NLV)
- New Living Translation (NLT)
- New Matthew Bible (NMB)
- New Revised Standard Version (NRSV)
- New Revised Standard Version Catholic Edition (NRSVCE)
- New Revised Standard Version, Anglicised (NRSVA)
- New Revised Standard Version, Anglicised Catholic Edition (NRSVACE)
- New Testament for Everyone (NTE)
- Orthodox Jewish Bible (OJB)
- Revised Geneva Translation (RGT)
- Revised Standard Version (RSV)
- Revised Standard Version Catholic Edition (RSVCE)
- The Message (MSG)
- The Voice (VOICE)
- Tree of Life Version (TLV)
- World English Bible (WEB)
- Worldwide English (New Testament) (WE)
- Wycliffe Bible (WYC)
- Young's Literal Translation (YLT)
Table of Contents
Main Menu
- Ancient Assyrian Social Structure
- Ancient Babylonia
- Ancient Canaan During the Time of Joshua
- Ancient History Timeline
- Ancient Oil Lamps
- Antonia Fortress
- Archaeology of Ancient Assyria
- Assyria and Bible Prophecy
- Augustus Caesar
- Background Bible Study
- Bible
- Biblical Geography
- Fallen Empires - Archaeological Discoveries and the Bible
- First Century Jerusalem
- Glossary of Latin Words
- Herod Agrippa I
- Herod Antipas
- Herod the Great
- Herod's Temple
- High Priest's in New Testament Times
- Jewish Literature in New Testament Times
- Library collection
- Map of David's Kingdom
- Map of the Divided Kingdom - Israel and Judah
- Map of the Ministry of Jesus
- Matthew Henry Bible Commentary
- Messianic Prophecy
- Nero Caesar Emperor
- Online Bible Maps
- Paul's First Missionary Journey
- Paul's Second Missionary Journey
- Paul's Third Missionary Journey
- Pontius Pilate
- Questions About the Ancient World
- Tabernacle of Ancient Israel
- Tax Collectors in New Testament Times
- The Babylonian Captivity
- The Black Obelisk of Shalmaneser
- The Books of the New Testament
- The Court of the Gentiles
- The Court of the Women in the Temple
- The Destruction of Israel
- The Fall of Judah with Map
- The History Of Rome
- The Incredible Bible
- The Jewish Calendar in Ancient Hebrew History
- The Life of Jesus in Chronological Order
- The Life of Jesus in Harmony
- The Names of God
- The New Testament
- The Old Testament
- The Passion of the Christ
- The Pharisees
- The Sacred Year of Israel in New Testament Times
- The Samaritans
- The Scribes
Ancient Questions
- Why Do the Huldah Gates Appear Different in Ancient Replicas and Modern Photos?
- What Is the Origin of the Japanese and Chinese Peoples? A Biblical Perspective
- How did the ancient Greeks and Romans practice medicine and treat illnesses?
- What were the major contributions of ancient Babylon to mathematics and astronomy?
- How did the ancient Persians create and administer their vast empire?
- What were the cultural and artistic achievements of ancient India, particularly during the Gupta Empire?
- How did ancient civilizations like the Incas and Aztecs build their remarkable cities and structures?
- What were the major trade routes and trading practices of the ancient world?
- What was the role of slavery in ancient societies like Rome and Greece?
- How did the ancient Mayans develop their sophisticated calendar system?
Bible Study Questions
- Why Do Christians Celebrate Christmas?
- How Many Chapters Are There in the Bible?
- The Five Key Visions in the New Testament
- The 400-Year Prophecy: Unpacking Genesis 15 and the Journey of a People
- The Authorized (King James) Version (AKJV): Historical Significance, Translation Methodology, and Lasting Impact
- Exploring the English Standard Version (ESV): Its Aspects, Comparisons, Impact on Biblical Studies, and Church Use
- A Detailed Historical Analysis of Language Updates in the KJ21: Comparison with Other Versions
- A Detailed Historical Analysis of the American Standard Version (ASV): Comparison to the King James Version, Influence on Later Translations, and Evaluation of Strengths and Weaknesses
- A Detailed Historical Analysis of Amplifications in the Amplified Bible (AMP) and Its Comparison to Other Bible Translations
- Detailed Historical Analysis of the Amplified Bible Classic Edition (AMPC): Examples of Amplifications and Comparative Analysis with Other Bible Translations
About
Welcome to Free Bible: Unearthing the Past, Illuminating the Present! Step into a world where ancient history and biblical narratives intertwine, inviting you to explore the rich tapestry of human civilization.
Discover the captivating stories of forgotten empires, delve into the customs and cultures of our ancestors, and witness the remarkable findings unearthed by dedicated archaeologists.
Immerse yourself in a treasure trove of knowledge, where the past comes alive and illuminates our understanding of the present.
Join us on this extraordinary journey through time, where curiosity is rewarded and ancient mysteries await your exploration.
Recent posts
-

Guest Posting in SEO: A Practical Marketer’s Guide to Links, Authority, and Safer Publishing
Guest posting can still be a smart way to build visibility, relationships, and referral traffic—but only when it’s done with real editorial value ... -

Religion in the U.S.: Where Belief Is Quietly Changing
Religion in the United States is not disappearing, but it is gradually reshaping itself in ways that are easy to overlook. Public debates often focus ... -

Best Free Microsoft Office Alternatives in 2026
Microsoft Office is the standard of productivity but not all can afford its subscription model. Luckily, there are free alternatives that will provide... -

João Cotrim de Figueiredo: A Journey from Business Leader to Presidential Hope for a Modern Portugal
João Cotrim de Figueiredo (full name: João Fernando Cotrim de Figueiredo), born on June 24, 1961, in Lisbon, Portugal, is a prominent Portuguese bus... -

Modern Christian Abstract Art Canvas Prints | Artesty
Modern Christian Abstract Art: Contemporary Spiritual Wall Art for a Modern Home Modern Christian art makes it easier to bring faith into everyday spa...